Duodenal Switch Surgery
The
Duodenal Switch procedure is one of the most effective weight loss procedures for the
treatment of diabetes and patients with a very
high body mass index. This procedure consists of restrictive and malabsorptive surgical techniques. First, the restrictive component involves reducing the size of the stomach to limit food intake and a longer duration of satiety. Next, the malabsorptive component involves the rearrangement of the small intestine which allows food to bypass so that fewer calories and nutrients are absorbed.
How it works
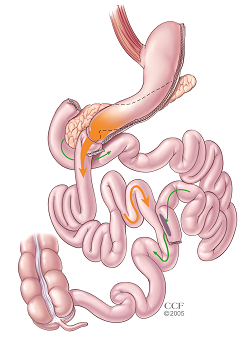

The duodenum, first portion of the small intestine, is divided just past the opening of the stomach. The surgeon uses surgical staples to form a small gastric pouch in the upper part of the stomach. A section of the end of the small intestine is then brought up and connected to the opening of the newly created stomach. Then when the patient eats, the food travels through the new stomach emptying directly into the last section of the small intestine. Unlike the other procedures, about three-fourths of the small intestine is bypassed by food. The rerouting and reconnection of the small intestine creates a significate decrease in the number of calories and nutrients absorbed since the food does not mix with the bile and pancreatic enzymes, imperative for the breakdown and absorption of fat and protein, until very far down the small intestine. Following surgery, you will meet with a dietician to discuss short-term and long-term nutritional needs.
The Duodenal Switch procedure primarily assists in reducing the amount of food that is consumed, however, over time this effect decreases and patients are eventually able to consume close to “normal amounts of food. Similar to the gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, this procedure affects blood sugar control and guts hormones which control appetite and fullness.
Photo source: Texas Health Bariatric Surgery - Website
Surgery Results
- The results are greater weight loss than Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy, or Adjustable Gastric Band - 60 – 70% excess weight loss or greater, at 5 year follow up
- The procedure eventually allows patients to eat near “normal” meals
- It reduces the absorption of fat by 70% or more
- It causes favorable changes in gut hormones to reduce appetite and feel fuller longer
- It is most effective for the treatment of diabetes compared to Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy, or Adjustable Gastric Band
Potential Patient Concerns
- It has higher complication rates and risk for mortality than the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy, or Adjustable Gastric Band
- Requires a longer hospital stay than the Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy or the Adjustable Gastric Band
Call us to schedule for a consultation today, (302) 892-9900.


